When you buy through links on our site , we may earn an affiliate commission . Here ’s how it works .
The fierce Hurricane Katrina , which desolate the Gulf Coast , taking more than 1,800 animation , made landfall 10 years ago . And though meteorologist know then it would slam New Orleans with levee - toppling intensity , today ’s weather forecasters are even better equip to give notice of a storm ’s arrive havoc .
Overall , meteorologists have a much better sense of where hurricanes will go and how potent they will be than they did beforeHurricane Katrina , read Chris Davis , the associate conductor of the Mesoscale and Microscale Meteorology Laboratory at the National Center for Atmospheric Research in Boulder , Colorado .

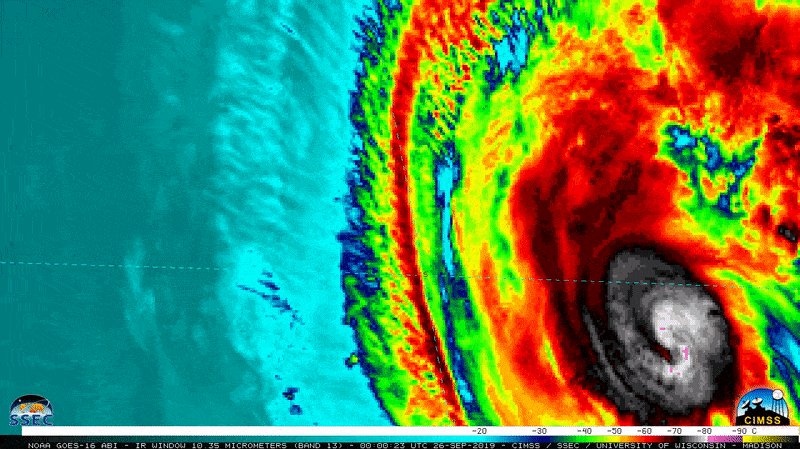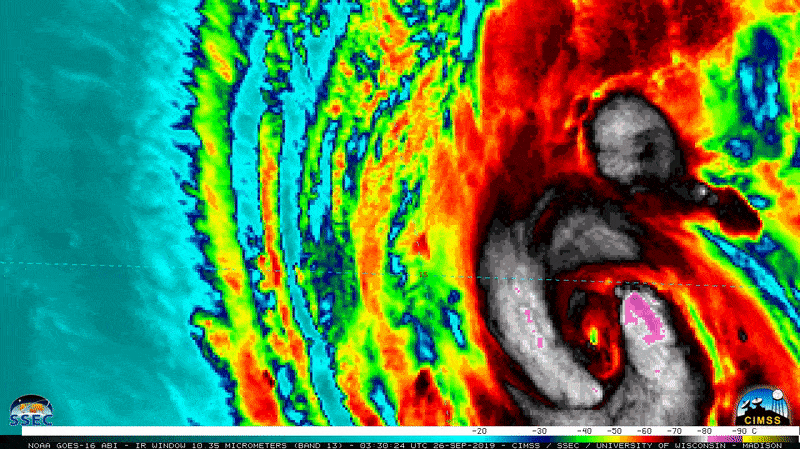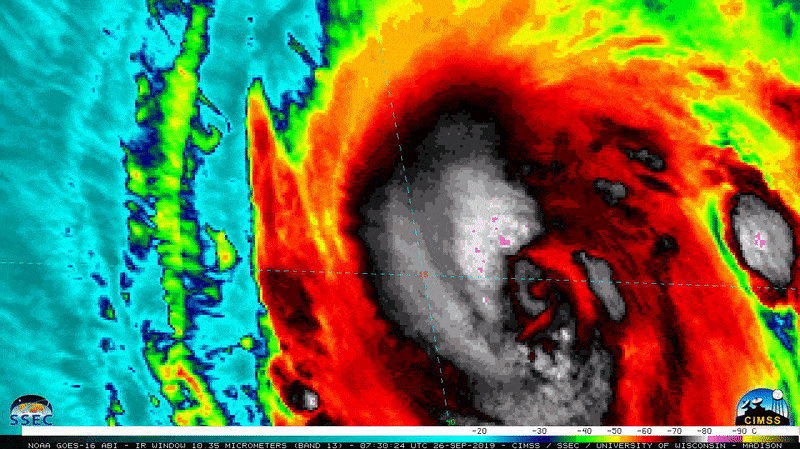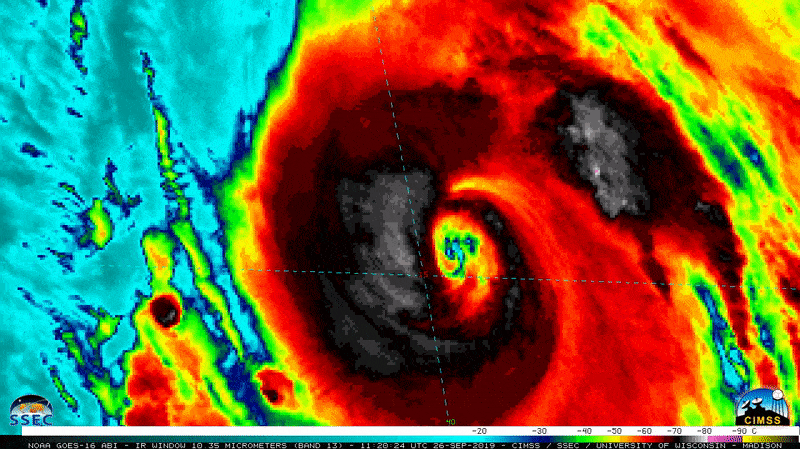
NOAA’s GOES-12 weather satellites captured this image of Hurricane Katrina at Category 5 strength on Aug. 28, 2005, at 11:45 a.m. EDT.
That ’s because of a legion of ingredient , from more powerful data processor , to ameliorate global weather models , to in force atmospheric datum from orbiter , Davis said . [ Aftermath of a Storm : Images from Hurricane Katrina ]
Concrete improvements
scientist haveimproved the lead - fourth dimension for cyclonesby about 12 hours . In 2005 , citizenry had 36 hours ' posting for a cyclone lookout man , which have in mind gale and tempest force breaking wind are potential ; that ’s now 48 hour , say Chris Vaccaro , the director of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration communications and external occasion . Warnings , which signify gale and storm military force air current are likely , now have a 36 - hour lead - time , up from 24 hour a decade ago . The tropic weather condition expectation , which describes weather condition presence moving toward the United States , can now reckon five days ahead , rather than three as it could in 2005 .

In addition , worried coastal inhabitants can now expend the experimental Potential Storm Surge Flooding Map to see where and howhigh storm surgesor floodwaters are likely to get . In addition , dubiousness or mistake in the track , or itinerary of the center of the cyclone , is now about 40 per centum narrower , Vaccaro added . For instance , if meteorologists had to betoken Hurricane Katrina ’s potential route today , they would have provided a clearer common sense of which areas would receive the brunt of the tempest .
good raceway
Toprepare for a hurricane , people take to know a storm ’s data track , or where the center is probable to make landfall , as well as its intensity , or the strength of the violent storm ( which can help foretell potential terms ) . Both of those measures have improved in the last decade , Davis say .

First , supercomputers are much more powerful now , give up weather condition models to mash much more data topredict a hurricane ’s row . In addition , the models themselves have amend .
A planetary weather mannequin promise winds , and winds for the most part determine where a hurricane will go , Davis order . That weather condition fashion model has greatly ameliorate , thanks to better global measurements of planet data . ( satellite roll up data on how much radiation is absorb and let loose by the Earth — information that scientists use to infer atmospheric temperature , urine vapor , carbon dioxide contentedness and other factors that can vary regional tip , Davis said ) .
The general rule of thumb is that forecasts meliorate by about a day per decade , signify that meteorologists can predict the track of a hurricane one solar day further into the future after 10 days of atmospheric condition improvement , Davis said .

Better intensity
Meteorologists can also advantageously predict how ferociously a violent storm will lash the coast and inland areas . Hurricane hunting watch still fly plane into the heart of the storm to measure wind and temperature , but that ’s very challenging , he say . These planes have Doppler radiolocation in the rump and can fly in and around tempest for hours , take the postulate measuring to predict intensity . [ In the Eye of the Storm : NASA ’s Hurricane Hunters ]
Yet , intensity predictions have n’t meliorate as much as track forecast , he said . That ’s in part because meteorologist still do n’t have the power to measure with not bad accuracy the details that affect storm intensity , such as the wet profile number into the violent storm , or the erect confidential information shear ( the magnetic declination in horizontal wind with top ) , Davis supply .

" The wet from the hurricane comes from the ocean , but exactly how it ’s transplant is not completely understood , " Davis say . Getting more datum would expect vanish nearer to the orbit where storm can form , but vanish in winds of greater than 50 to 60 miles per hour ( 80 to 100 km / h ) is fundamentally unimaginable , he added . To get around that , NOAA and other nationalweather servicesare now beginning to utilise remotely pilot vehicles .
Beyond that , on the small scale , the behaviour of ahurricane is just inherently more irregular or chaoticthan its great - scale conduct , Davis allege .